Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Oba, Hirofumi; Narumi, Issei
no journal, ,
To investigate the role of the RecFOR pathway in DNA double-strand break (DSB) repair in  , we generated a
, we generated a 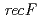 disruptant strain and characterized the disruption effect. The
disruptant strain and characterized the disruption effect. The 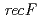 disruptant strain exhibited hypersensitivity to
disruptant strain exhibited hypersensitivity to  rays than the wild-type strain. PFGE analysis showed that genome restitution ability following irradiation was severely impaired in the
rays than the wild-type strain. PFGE analysis showed that genome restitution ability following irradiation was severely impaired in the 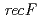 disruptant strain, suggesting that RecF has a crucial role in DSB repair. Furthermore, following irradiation, induction of RecA, which is essential protein for DNA recombination repair, was observed in the
disruptant strain, suggesting that RecF has a crucial role in DSB repair. Furthermore, following irradiation, induction of RecA, which is essential protein for DNA recombination repair, was observed in the 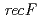 disruptant strain just as the wild-type strain. However a large amount of RecA protein in the
disruptant strain just as the wild-type strain. However a large amount of RecA protein in the 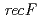 disruptant strain remained inactive following irradiation. We suppose that the defect in RecA activation resulted in hypersensitivity to ionizing radiation and failure to repair radiation-induced DSB in the
disruptant strain remained inactive following irradiation. We suppose that the defect in RecA activation resulted in hypersensitivity to ionizing radiation and failure to repair radiation-induced DSB in the 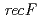 disruptant strain.
disruptant strain.

Sato, Katsuya; Kikuchi, Masahiro; Narumi, Issei; Oba, Hirofumi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English

Wadachi, Hiroki*; Kunieda, Takekazu*; Abe, Wataru*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Watanabe, Masahiko*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; Higashi, Seigo*; Okuda, Takashi*
no journal, ,
We collected some kinds of tardigrade to develop multi-cellular model oraganism for extremotolerant. Among four kinds of collected tardigrade, we found that a tardigrade  at Sapporo-city feeded
at Sapporo-city feeded 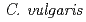 and could breed. The life-time of
and could breed. The life-time of 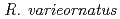 in an artificial culture condition is about 35 days and 5.7 days for hatching. During the whole life-time, one animal laids 8 eggs. In addition, it was observed that
in an artificial culture condition is about 35 days and 5.7 days for hatching. During the whole life-time, one animal laids 8 eggs. In addition, it was observed that 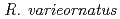 could enter an ametabolic dry state called anhydrobiosis in all stages of life-time. Furthermore, we observed a high surviving-rate even if
could enter an ametabolic dry state called anhydrobiosis in all stages of life-time. Furthermore, we observed a high surviving-rate even if 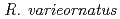 exposed in various kinds of extreme environments.
exposed in various kinds of extreme environments.

Wadachi, Hiroki*; Kunieda, Takekazu*; Sakashita, Tetsuya; Kawai, Kiyoshi*; Iwata, Kenichi*; Nakahara, Yuichi*; Hamada, Nobuyuki*; Koseki, Shigenobu*; Yamamoto, Kazutaka*; Kobayashi, Yasuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
We studied the effects of the exposure of extreme environments on life-time and breeding ability of tardigrade 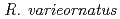 to reveal the possibility of multi-cellular organism existences in the outerspace. A life time of animals is the shortest in the heavy-ion exposed animals than any other stressors. There were significant decrease in the number of egg-laying and hatching rate between irradiated and non-irradiated animals. However, we found the next generation in all experimental conditions. Our findings suggest that tardigrades exposed to even any extreme environments could have a descendant.
to reveal the possibility of multi-cellular organism existences in the outerspace. A life time of animals is the shortest in the heavy-ion exposed animals than any other stressors. There were significant decrease in the number of egg-laying and hatching rate between irradiated and non-irradiated animals. However, we found the next generation in all experimental conditions. Our findings suggest that tardigrades exposed to even any extreme environments could have a descendant.